Solution for Section G.1 Question 2
2. The four group properties are satisfied.
Let the elements of Z7 be represented by [0], [1], [2], [3],
[4], [5], [6]. To add these elements modulo 7, you add the numbers and
then reduce your result modulo 7.
Closure For all x,y
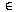 Z7 we have x + y
Z7 we have x + y
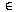 Z7 and so Z7 is closed under addition modulo 7.
Z7 and so Z7 is closed under addition modulo 7.
[0]+[0]=[0] [0]+[1]=[1] [0]+[2]=[2] [0]+[3]=[3]
[0]+[4]=[4] [0]+[5]=[5] [0]+[6]=[6]
[1]+[0]=[1] [1]+[1]=[2] [1]+[2]=[3] [1]+[3]=[4]
[1]+[4]=[5] [1]+[5]=[6] [1]+[6]=[0]
[2]+[0]=[2] [2]+[1]=[3] [2]+[2]=[4] [2]+[3]=[5]
[2]+[4]=[6] [2]+[5]=[0] [2]+[6]=[1]
[3]+[0]=[3] [3]+[1]=[4] [3]+[2]=[5] [3]+[3]=[6]
[3]+[4]=[0] [3]+[5]=[1] [3]+[6]=[2]
[4]+[0]=[4] [4]+[1]=[5] [4]+[2]=[6] [4]+[3]=[0]
[4]+[4]=[1] [4]+[5]=[2] [4]+[6]=[3]
[5]+[0]=[5] [5]+[1]=[6] [5]+[2]=[0] [5]+[3]=[1]
[5]+[4]=[2] [5]+[5]=[3] [5]+[6]=[4]
[6]+[0]=[6] [6]+[1]=[0] [6]+[2]=[1] [6]+[3]=[2]
[6]+[4]=[3] [6]+[5]=[4] [6]+[6]=[5]
Associativity
For all x,y,z
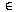 Z7 we have (x + y) + z = x + ( y + z) since addition is
associative.
Z7 we have (x + y) + z = x + ( y + z) since addition is
associative.
Identity
For all x
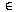 Z7 we have x + [0] = x = [0] + x. Hence [0] is the identity
element under addition modulo 7.
Z7 we have x + [0] = x = [0] + x. Hence [0] is the identity
element under addition modulo 7.
Inverse
For all x
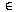 Z7 we have x + (7-x) = [0] = (7-x) + x, where 7-x is the usual
operation of subtraction on the integers.
Hence 7-x is the inverse of the element x.
Z7 we have x + (7-x) = [0] = (7-x) + x, where 7-x is the usual
operation of subtraction on the integers.
Hence 7-x is the inverse of the element x.
We can explicitly give the inverses:
[0]-1 = [0];
[1]-1 = [6];
[2]-1 = [5];
[3]-1 = [4].
[4]-1 = [3];
[5]-1 = [2];
[6]-1 = [1].
Notice that in any group, the inverse of the inverse of an element x is x;
that is, (x-1)-1 = x.
Back to Section G.1